The healing effects of music on the brain.
Have you ever wondered why you feel good with music that resonates with you?
Why do certain types of music provide an emotional uplift, a state of relaxation, or cognitive enhancement whilst others make you spin in frustration?
What happens in the brain when we play a musical instrument or listen to music?
The purpose of this article.
As a musician and healer, I have always been fascinated with how music and sound has an impact on our well being. As a result, I have been running this website since 2015.
The website has provided me with a platform to both enhance and share my learnings. So effectively, all the articles, meditation videos and healing music I have created and shared on this website are a result of healing practices that have personally worked for me.
I have been studying the concept of how the brain works with music and sound for a few years and discovered that the more I understood the concept the more I could assist my own health needs and practice as a healing musician.
I have been searching for various sources of information on how music affects the brain and came across many useful books and online posts.
However, due to the complexities of the subject, I struggled to find something that was clear, concise and within a simplistic form of presentation.
So about a year ago, I decided to start pulling together my learnings and personal discoveries and create an article in my interpretation that I can share. And so here it is 🙂

What I hope this article can bring to you.
My aim is to provide you with useful information to help you further understand how the brain reacts to the various types of music available, so you can choose how to utilise the power of music to support your well-being.
I have written the article in a form suitable for readers new to the subject.
There are a variety of topics within this article which are organised in sub-sections shown within the table of contents below. These sub-sections are interrelated and describe how music affects the brain and our behaviours in different ways.
The article is supported by visual representations to aid the reading process.
You can either view the sections that feel relevant to you or read the whole article.
I welcome you to book mark this page as I will continue to develop the information.
I also welcome your feedback or questions within the social area located near the bottom of the page.
In the meantime, I wish you health and happiness.
Paul Darren Grout.
Table of contents
The healing effects of music on the brain
What parts of the brain are stimulated by music?
The main areas of the brain & their primary functions
Key individual components of the brain
How music stimulates the right & left hemispheres
What is Brain Entrainment?
What are brain waves?
How sound travels to the brain
How different Music Genres Affect the Brain, Mood & Behaviour
Your Personal Music Choices
Safety tips on listening to music
Conclusions & Recommendations
What I do as a Quantum Healing Musician.
The healing effects of music on the brain
Music is an effective therapeutic and mood-altering tool that is easily accessed.
The activity of listening, creating, playing or reading music involves many brain components to operate simultaneously.
Lets go into greater detail.
Music can provide the following:
- Facilitate neurogenesis which is the repair and regeneration of cerebral nerves leading to cerebral plasticity for increased alertness and cognitive abilities.
- Stimulate the formation of the happy brain chemical dopamine which plays a role in the reward system and contributes towards arousal, motivation and feeling good.
- Reduce the cortisol hormone known as the body’s stress hormone.
- Increase the production of the Oxytocin, which has a positive impact on social behaviour, bonding and trusting other people.
- Alter brain wave patterns (more about this below). For example, soothing music helps induce alpha brain waves associated with calmness and relaxation.
– When our brain wave frequency changes to alpha, we put ourselves in an ideal mind condition to learn new information, perform elaborate tasks, learn languages and analyse complex situations.
7. Connect the left and right brain hemispheres for increased information storage and creative imagery.
– When listening to music neurons are activated in the corpus callosum that stimulates both sides of the brain at the same time. This can also permit the release of endorphins like serotonin that provide a sense of well-being and relaxation.
What parts of the brain are stimulated by music?`
Music is structural, mathematical and architectural and based on the relationships between one musical note to another. Therefore, music engages the brain at almost every level.
The rhythm, pitch, tone and melody of music activates the brain in many different ways.
So the brain has to do a lot of work to make sense of it.
Before we go into greater detail with the various brain components, I would like to provide some examples of how the brain becomes stimulated by music during certain activities:
- Listening to music involves the brain’s memory centres, such as the hippocampus and lowest parts of the frontal lobe. Listening to or recalling lyrics will involve language centres in the temporal and frontal lobes.
- Dancing or tapping your feet along with music gets your cerebellum involved.
- Reading music involves the visual cortex.
- When performing music on a musical instrument, the frontal lobe (planning part of the brain) and your motor and sensory cortex activate. Playing music requires the coordination of motor control, somatosensory touch and processing of auditory information.
The main areas of the brain and their primary functions
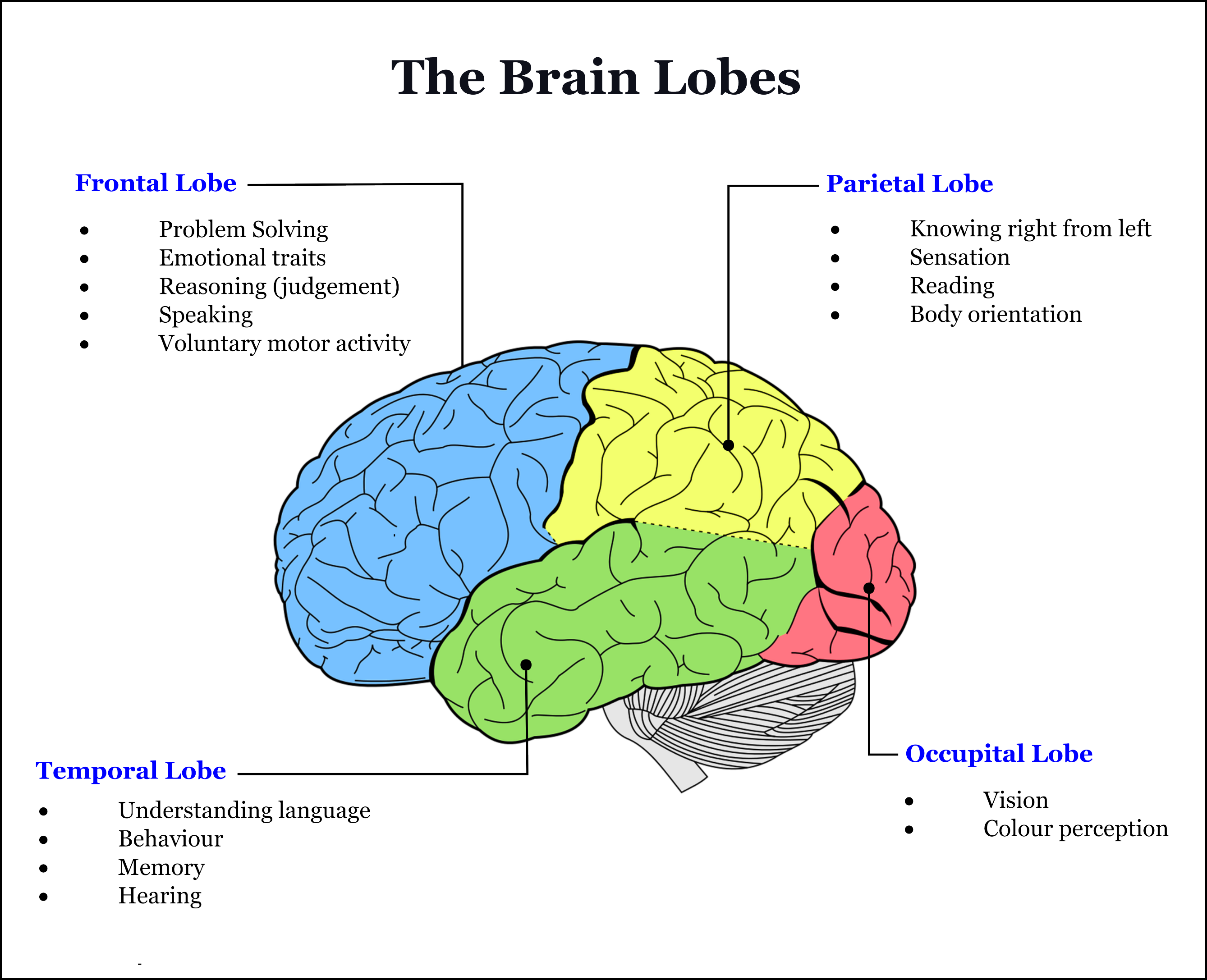
The main four parts of the brain are the frontal lobe, temporal lobe, parietal lobe and occipital lobe.
When music enters the brain, all four parts work on different aspects making various brain components (within these main areas) become engaged and activated.
Music does not follow one path within the brain and is processed in many complex ways as music has many elements that frequently change, such as tempo, rhythm, melody and tone.
The anatomy of the brain is a vast and complex subject. So the purpose of this article is to highlight components of the brain to provide you with a basic idea of how the brain processes sound and music.
The Lobes (main parts of the brain)
The brain has four main areas called the Lobes.
The Frontal Lobe – located a the front manages skills for solving problems, planning, making decisions and controlling behaviour. A region within the Frontal Lobe enables the mind to construct the syntax for music and language. For example, identifying whether a beat is steady or the melody makes sense.
The Temporal Lobe located at the sides of the brain near the temple is the home of the auditory system for processing what we can hear. It also plays a part in object recognition, memory storage, and the use of language.
The Parietal Lobe is positioned above the occipital lobe and behind the frontal lobe. Its primary function is to integrate the incoming sensory information for touch and pain.
The Occipital Lobe processes what we see. Music light’s up the imagination.
Refer to the below image to view the locations of the four brain lobes.
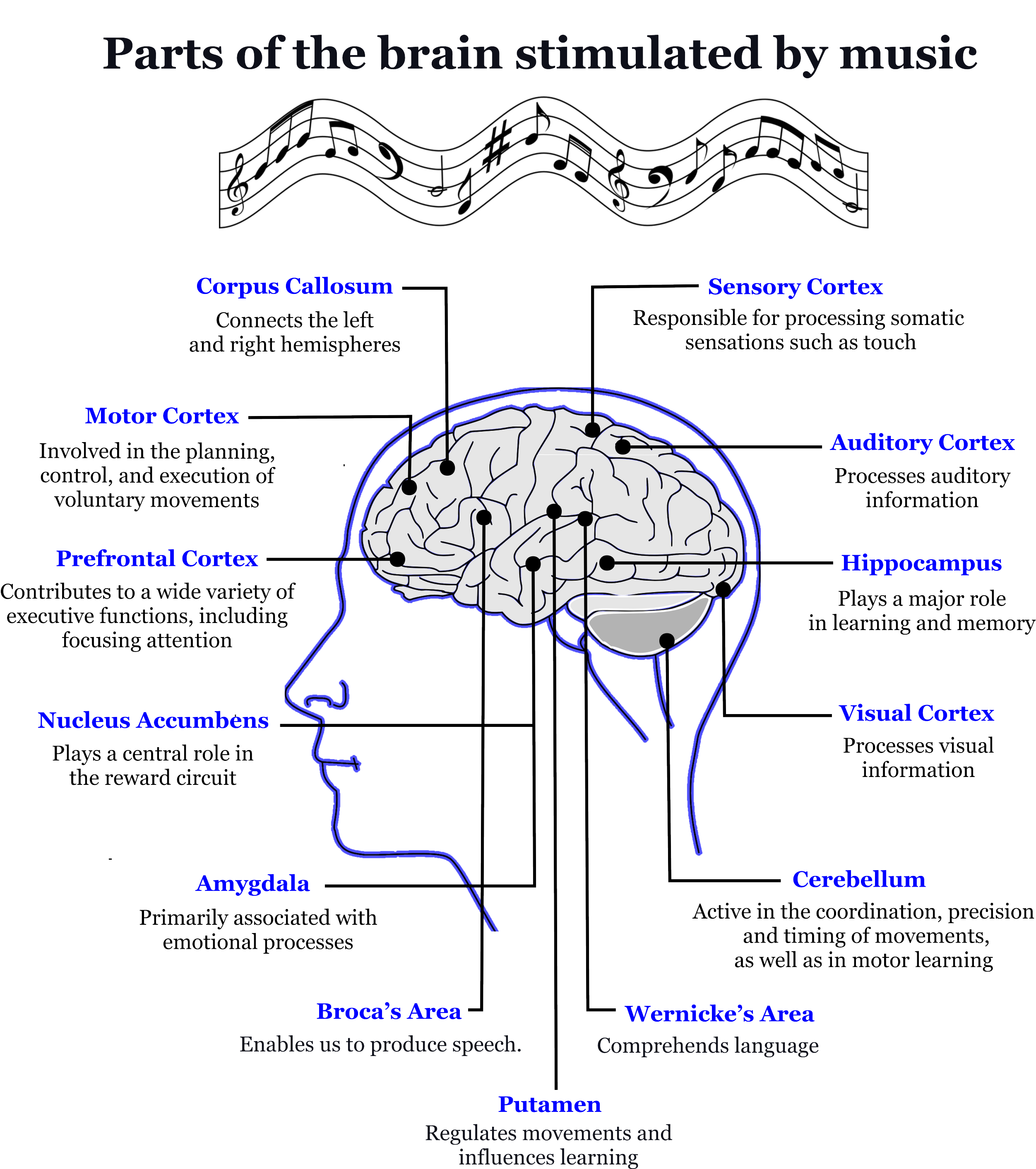
Key individual components of the brain
Auditory Cortex – located within the Temporal Lobe processes information retrieved from the ears. This section plays a part in the recognition and understanding of pitch, tone, melody and harmony.
Amygdala – plays a part in processing emotions. Music can trigger emotional responses in a more direct way than any other stimulus. The Amygdale is held within the Temporal Lobe.
The Hippocampus – within the Temporal Lobe produces and retrieves memories, regulates emotional responses, and helps navigation. Music activities memories that the temporal lobe stores and recalls.
Hypothalamus – maintains the body’s status quo, links the endocrine and nervous systems, and produces and releases essential hormones and chemicals that regulate thirst, appetite, sleep, mood, heart rate, body temperature, metabolism, growth and sex drive. The Hypothalamus is near the Hippocampus.
Nucleus Accumbens – located within the basal forebrain, releases the neurotransmitter dopamine associated with pleasure and reward.
The Corpus Callosum – stretches across the midline of the brain, enables the left and right hemispheres to communicate to allow coordinated body movements and complex thoughts that require logic (left side) and intuition (right side).
The Putamen – located at the base of the forebrain, processes rhythm and regulates body movement and coordination.
Prefrontal Cortex – covers the front part of the frontal lobe is involved in planning complex cognitive behaviour.
The Belt and Parabelt – located on the right side of the brain, are responsible for figuring out a song’s rhythm. When creating rhythm by tapping toes or beating a drum, the motor cortex and cerebellum become involved.
Broca’s Area – enables us to produce speech. We use this part of the brain to express songs and singing.
Wernicke’s Area – comprehends written and spoken language. We use this part of the brain to analyse and enjoy music.
Musical activities such as reading music, playing an instrument, and dancing tend to fire up the cerebellum, motor cortex, sensory cortex, and visual cortex, as detailed below.
The Cerebellum – located at the back of the brain – coordinates movement (like dancing) and stores physical memory.
Motor Cortex – found on the frontal lobe is involved in the planning, control and execution of voluntary movement.
Sensory Cortex – positioned within the anterior part of the parietal lobe (immediately behind the frontal lobe) is connected to our sense of touch.
Visual Cortex – held within the occipital lobe, the primary purpose of the visual cortex is to process visual information such as reading musical scripts or lyrics.
The areas of the brain stimulated are dependant on the activity undertaken, for example, listening, reading, creating or playing music
The image below shows the various brain components stimulated by music and their primary functions for a human being.
Please note that the image provides a rough guide for the actual positions of the named brain areas.
How music stimulates the right and left hemispheres.
Modern research has shown that music allows both hemispheres (left and right sides of the brain) to work together. So a lot of brainpower is activated through listening and performing music.
The left side of the brain contains specific components that support analytical, logical and intellectual thought processes, and the right side holds the subjective-artistic and intuitive parts of the brain.
The right hemisphere is also responsible for controlling the left side of the body, whilst the left hemisphere controls the right side of the body.
The Corpus Callosum (located underneath the cerebrum) is a structure that allows both the left and right sides of the brain to communicate together.
When listening or performing music, neurons (information messengers which transmit information) become activated within the Corpus Callosum. This enhanced brain activity enhances its processing power on many levels. For example, increased storage of information, creative imagery, and the release of endorphins like serotonin give a sense of well-being and relaxation.
Musicians are known to have larger Corpus Callosums’ than those of non-musicians. The regularity of playing music on musical instruments develops this component of the brain in many ways.
What is Brain Entrainment?
Music has the power to lead the mind into various states. This is because our brain waves become synchronised through sound and music through what is called entrainment.
Entrainment is defined as “the effect of one system on another.”
The scientific explanation for entrainment is that any two vibrating bodies will try to synchronise with each other.
If you put several pendulum clocks on the wall and set them to swing at different rates, they will eventually become synchronised and move in unison.
Specific sound vibrational frequencies sent to the ears will eventually entrain the brain into specific states.
For example, meditative music can push the mind towards a more trance state to enhance focus, relaxation or sleep.
What are brain waves?
Brainwaves are electrical impulses in the brain that occur at various frequencies which resonate at different speeds.
The brain uses these electric signals to process, organise and communicate the information it receives. So our brain waves change in accordance with the information it processes. Therefore, brain waves alter with the type of music and sound it is exposed to.
Our brainwaves change according to what we are doing and feeling at the time. Our thoughts, emotions and behaviours are affected by the communication between neurons within our brains.
We generally have a mixture of various brainwaves occuring all the time. However, one brainwave state will be more actively dominant than the others at any given time.
With an understanding of the role of the various brainwaves, we can make decisions to alter our brain waves through music to support our desired mental states and optimal functional behaviours.
The five different brain wave frequencies and their specific roles are as follows:
- Gamma – Considered to be the fastest brain activity is responsible for cognitive functioning, learning, memory, and information processing. The prominence of this particular wave leads to high arousal, anxiety, stress states. In optimal conditions, gamma waves help with attention, focus, and the binding of senses.
- Beta – This is associated with our normal and everyday state of alertness. For example, conscious logical thinking, analysis and active attention.
- Alpha – Occurs during daydreaming and creative visualization. It is a relaxed state which is generally associated with right-brain thinking and the subconscious mind. Alpha frequencies also encourage relaxation, a decrease of anxiety and an increase of positivity, concentration, problem-solving and improved memory.
- Theta – Is activated during dream sleep and deep meditational states. Theta is also associated with creative thinking and allows us to tap into our inner genius, deeper subconscious to superconscious. This state allows access to insights, bursts of creative ideas through vivid imagery.
- Delta – Normally associated with deep sleep and no thinking. A key state for regeneration and rejuvenation.
How SOUND travels to the brain
Sound waves travel onto the outer ear and pass through to the middle ear where the sound waves cause the eardrum and tiny bones to vibrate.
The middle ear then passes these vibrations onto the inner ear where the vibrations stimulate thousands of tiny hair cells.
The tiny hair cells in our inner ear generate electrical signals to the auditory nerve system which is connected to the auditory centre of the brain.
The auditory centre processes the electrical impulses which are then are perceived by the brain as sound. So the brain translates the impulses into sounds that we know and understand.
How DIFFERENT Music Genres Affect the Brain, Mood & Behaviour
In the modern age of music, there are thousands of different genres in existence.
The purpose of this section is to define the most popular styles of music and to highlight their potential effects on our productive mood and behaviour.
- Pop – a genre of popular music that commonly reaches the music charts. They often have a good rhythm, a catchy melody, and are easy to remember and sing along to. They are good for arousing emotions, dancing and picking up energetic moods. Listening to upbeat pop music can help increase motivation and reduce fatigue.
- Blues – An exuberant and simplistic type of music full of upbeat and slow rhythms, humour and emotional lyrics which often represent sadness, suffering and loneliness. Blues represents the heart and soul of life and encourages freedom of expression.
- Jazz – The key elements of Jazz includes a diversity of blues, swing, syncopation and creative freedom. Upbeat Jazz music is known to reduce negative emotions, as well as evoke happy and positive feelings and improve memory and focus. As Jazz music generally varies in the speed of rhythm the music can be either stimulating or relaxing to the listener.
- Rock – Often a driving, intense, energetic type of music which involves electric instruments along with strong lyrics and diverse sounds, The fast and loud beats of rock music encourages energetic liveliness and stimulation which can help with tasks such as workouts or other intense exercises.
- Country – Consists of ballads and dance tunes that are also simplistic within their form. Often consists of folk lyrics that are emotionally connected to love, loneliness, family, values, and living the hard life. A country song can either sadden you, especially if the songs are about heartbreak, or help you feel good about positively overcoming life dramas.
- Soul – Designed to convey strong emotions with typically deep meaningful lyrics. Its roots are from old gospel played in southern churches. It represents power through community and can evoke a stronger desire to survive and move forward in life.
- Dance – Uptempo, upbeat music intended for clubs with catchy songs with an easy, pop-based structure. As this particular music style encourages dance the physical movements alone will help you get rid of negative emotions, refresh your mind, and significantly improve your mood.
- Classical – Has characteristics of elegance through instrument melodies that have contrasting moods. Classical music is known to enhance brainpower through the relaxing sounds from string instruments. The calming effect releases dopamine for improved mood. Classical music is also known to encourage mind clarification to make tasks such as writing and studying more enjoyable.
- Ambient – Emphasizes tone and atmosphere over traditional musical structure or rhythm which may have elements of new-age and drone music. A form of instrumental music that may lack net composition, beat, or structured melody. Some recordings use sustained or repeated notes. Ambient music is known to reduce stress and anxiety while improving performance, focus and brain function. A good deal of popular meditation music features elements of ambient music.
- Mediative – Specifically developed to aid the practice of mindfulness activities such as meditation and yoga. Recordings are often slow-paced, instrumental recordings developed to calm the mind, enhance focus and relax the body. It is common for meditation music to combine multiple different types of styles or techniques into one tune or song. For example, they may contain elements of vocal chant recordings, slow melodic instrumentals, binaural beats, solfeggio frequencies, isochronic tones and background sounds of nature.
Your Music preferences
Although music, in general, is of personal preference it is a good idea to experiment with various music styles to discover the various effects they have on your thought patterns, emotions and overall mood.
Although music has powerful healing effects, it is important to also consider how emotional songs can affect people in different ways.
Songs and music can also activate psychological triggers related to past traumatic memories which can bring up feelings such as grief and sadness and therefore, divert concentration and effectiveness. So this is why it is important to establish what best works for your work ethics.
If you have a physically active job or exercising at a gym you might want to consider playing some pop, rock or dance music in the background to see if it helps boost motivation and physical positivity. Alternatively, if you are in a creative mood you might want to consider classical, jazz, ambient or mediative music.
Instrumental music in particular (without lyrics) has been increasingly popular within the modern age of office working. Such music is being used as background to help enhance performance on cognitive tasks, improve accuracy, and enable the completion of repetitive tasks more efficiently. Classical, ambient music and meditative music are known to commonly provide the best mood-boosting benefits, Provided the music has a soothing regular beat, it can help us to stay calm and relaxed.
As you discover music that bests suits your working style try using a music player to create your favourite playlists which contain music you most enjoy listening to during the various productive activities you undertake.
Spotify provides an excellent online resource for creating favourite playlists and saving them onto your devices.
Safety tips on listening to music
Music can bring joy to us all. However, like all things in life our human ears need to be looked after to ensure their longevity in health.
In general, sounds that are below 70 decibels (dBA) are considered safe. However, any sound at or above 85 dBA is more likely to damage your hearing over time.
Most modern phones and music players have preset volume limiter functions to ensure that the ears are not overexposed to the sound output, especially when using headphones. Have a look at the available settings on your devices to see if the volume settings are already preset for safety measures, or whether they need adjusting.
Sound quality matters. So if you are seeking the best experience with your music consider the type of headphones or speakers that would best suit your personal preferences and working environment. Consider the practicality, style, sensitivity and clarity of the sounds they produce. Poor quality output devices can induce a distracted mindset other than a pleasantly focussed one.
Consider whether the type of music you are listening to places you into a state that is suitable for the work activity you are performing. For example, it is best to avoid listening to music that activates the Theta and Delta brain waves (encourages the feeling of sleepiness) whilst driving or operating machinery.
Conclusions & Recommendations
I hope you are found this article useful for your personal needs.
In the meantime, here are some key points from the article on how music affects the brain along with some guidance:
- Music and sound effects the functionality of various brain components in many different ways. For example, Sound and music can activate hemispheric synchronization and increase brain processing power for improved concentration, enhanced learning capacity, and encourage a more positive mindset for personal success.
- Music has the power to alter brain waves to support desired mental states and behaviours. So with an understanding of the role of the various brainwaves, we can make informed decisions to create healthier and more functional behaviours within our lifestyles.
- Different genres of music can induce different effects on the mind and emotional wellbeing. Experiment with different genres of music to see how they affect you on a personal level. For example, consider the mental states you wish to experience and achieve whilst listening to music. Does the music help you feel calm, focussed or energetically motivated?
- Consider your safety during your work activities whilst listening to music. Consider how the various types of music affect your ability to work, create and concentrate safely,
- Although music, in general, is of personal preference it is a good idea to experiment with various music styles to discover the various effects they have on your thought patterns, emotions and overall mood. Develop a playlist of your favourite tunes within organised categories such as music for creativity, office work or physical working activities.
What I do as a Quantum Healing Musician.
Sound healing naturally assists your brain to steady its inner reactivity and so calm troublesome feelings of stress, anxiety, panic, frustration, hyper-alertness and distress.
As a Quantum Healing Musician, I create soothing piano compositions and meditations which aim to restore the natural healing frequencies of the mind and chakra energy centres to support a person’s life productiveness and wellbeing.
If you are not familiar with Chakras. These are energy centres or portals in the human energy field that receive and transmit energy and act as gates through which our life force flows in and out of our physical bodies. These energy fields can often become blocked because of physical, emotional, mental, traumas or spiritual disturbances. When Chakra’s become blocked we can often feel constricted or stuck in certain areas of our life. So Chakras require frequent rebalancing and recharging to function well.
I also identify the sounds and rhythms, which correspond to certain emotional responses and blockages and create pieces of music for the healing of all kinds of emotional and mental states. For example, I have created a series of music meditation videos (available on this website) to assist people to release emotional blockages, overcome stress and anxiety, empower self-love, forgiveness and create powerful intentions for personal success,
In addition, I create informative videos and articles on how music, rhythm and sound can be used as alternative therapeutic healing modalities.
To see examples of my work I welcome you to visit the website page Healing Music Videos & Articles.
Social engagement and questions for music and the brain
I welcome you to share your thoughts, feelings or ask questions within the social area below.
I also welcome you to bookmark this page as I will continue to review and update this article on a regular basis.

Article and images created by Paul Grout. Copyright © 2022 · Musicenergetics.net· All Rights Reserved. This article has been registered onto Copyright House.
Please read the disclaimer available on this page.





I look forward to responding to your views or any questions you have on this article.
This is a brilliant article on music and the brain. 7years ago encephalitis ruined my memory. I hate it. I thankfully don’t remember my time in hospital because I’ve been told I was asleep for quite some time and when I finally awoke my memory had been wiped, I’ve been told I didn’t even recognise my parents when I first awoke. I don’t understand how I could forget them. Thankfully 7years on I now have some old memory back up until about a year before it got me. I’m now back living with my parents unable to do my old job (was a systems tester for a website shop). and I’ve thought a great way to describe my illness is that I am like an old computer. All was going well I had good battery, good memory. Then one day I crashed. Memory was wiped. Am up and running again thankfully some old memory is back but any new memory has to be printed off (written down in my diary). Apart from music. Music had stayed and I’d be quite lost without it.
Also a wonderful plus now I can’t work is that I get to spend my Tuesdays with my Grandmother. She’s now in her 90s, bed bound and often appologising that I have to put up with an old lady that can’t do anything. I’ve tried to ban her from appologising. I thought where music has been good to me I’ll see if it helps her. So I asked her one day if we could put on some music but could she pick it because my silly memory couldn’t remember any. So we put on some 40s and for the first 10mins she spent the time just appologising that I had to sit and listen to all this old music but after a while I could see her just getting lost in the music and I myself enjoyed it a whole damn lot more than I expected so I was quite happy.
P.S. Appologies if I have already said this before but with my…wonderful…memory this is either the 1st or the 5th time
Dear Clair. Thank you for sharing. I am sorry to hear about your incident and the effects on you. It is good to know that you are on a healing path and how music and love from your family are helping the recovery process. I welcome you to look at my music meditation videos on the website, as they may also provide you with assistance. My regards to you and your family.